While
the war raged in Europe and Asia, it was quite a different story
here in the U.S.
In
1943, the U.S. living standard was 16% higher than it was in 1939.
Businesses prospered as wartime profits soared.
Large
businesses with huge government contracts supplied the medicine
that ailing economy needed.
When
the war started, not all American production was considered first
class: the Sherman tank was considered more vulnerable than the
German Tiger tank; Liberty Ships, hastily welded, were known to
break apart in heavy seas; U.S. torpedoes were known for malfunctioning.
A
story in one of the major magazines reported a frustrated U.S.
submarine crewman, with Japan's largest oil tanker in their sights,
hit the ship with 8 duds before running out of ammunition.
Most
of the American production was considered equivalent to their
counterparts. Where the U.S. was stunningly superior was the massive
amount of financing and production.
Bring
on the Women
Within
5 months after Pearl Harbor, 750,000 women volunteered for labor
jobs at production plants. Only 80,000 were taken because managers
of plants were so leary of using women workers.
By
1944, 3,500,000 women were on the assembly lines making tremendous
strides not only at maintaining production speed but greatly cutting
down on pre-war production time. For example, by 1944 production
time to make a bomber dropped from 200,000 man hours to 13,000.
In
the same month that Stalin was toasting the U.S. production, which
was about 6 months before the invasion of Normandy, factories
had built up such an enormous amount weapons that Washingto ordered
some factories to stop hiring and cut back on production.
Through
out 1944, government committees were drawing up plans to convert
factories to peace-time production.
Here's
the governments totals of factory production from July 1, 1940
until July 31, 1945:
| Aircraft |
296, 429 |
| Naval Ships |
71,062 |
| Cargo Ships |
5,425 |
| Artillery |
372, 431 |
| Small Arms |
20, 086, 061 |
| Small Arms ammo |
41,585,000,000 |
| Aircraft bombs |
5,822,000 |
| Tanks and propelled |
102,351 |
| Trucks |
2,455,964 |
At
the production plant shown below is a line of Corsairs - fighter
planes with the fold-up wings for use on aircraft carriers. Over
6,000 were made in this plant alone.
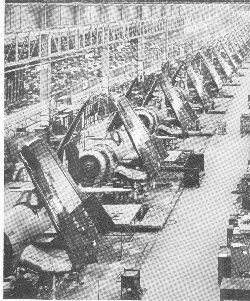
The
amazing thing is that at no time did military expenditures account
for more than 40% of the gross national product.


